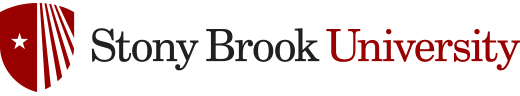Compressible Turbulence
Magnetic Reynolds Number Effects on MHD Turbulence
Ladeinde, F. and Gaitonde, D.V., Physics of Fluids 16 (6), pp. 1997-2021 (2004);
https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1736674
Abstract
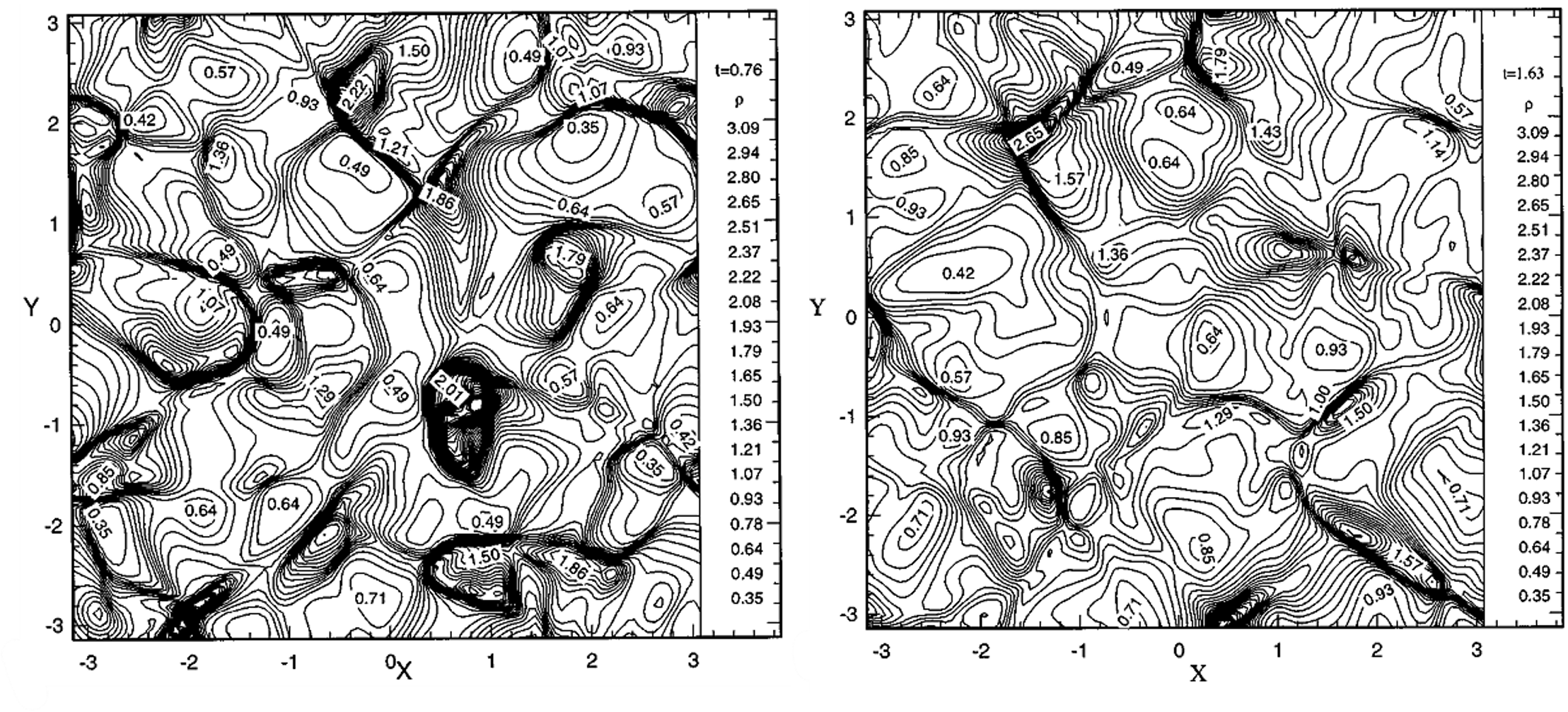
The effects of the magnetic Reynolds number, Re𝜎, on decaying two-dimensional compressible magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) turbulence are investigated through direct numerical simulations. The initial relative intensities
of, and the correlation between, the fluctuating velocity (u) and magnetic induction (b) fields are also varied, as measured with the respective parameters f and angle θ. The investigations cover the parameter ranges 1⩽Re𝜎⩽250, 0°⩽θ⩽90°, and 1⩽f⩽3. The results suggest that, at the lowest Re𝜎Reσ investigated, the magnetic field has a negligible impact on the evolution of the turbulence kinetic energy 𝐸𝑘. At higher Re𝜎 values, when magnetic effects are important, the magnetic field tends to accelerate the decay of the turbulence energy relative to non-MHD flows. On the other hand, the magnetic energy 𝐸𝑏 shows the opposite trend, being rapidly driven from its initial values to essentially
zero very early in the transient at lower Re𝜎 values, while higher Re𝜎 values significantly retard this decay. An enhancement of density fluctuations is
noted in the intermediate Re𝜎 range. An interesting observation pertaining to the normalized cross helicity is
the fast decay to zero of this quantity when Re𝜎=1, independent of the values of θ and f. That is, the fluctuating u and b fields tend to be uncorrelated when the magnetic Reynolds number is low. In this case, the role of the magnetic field is passive, and it is merely convected by the velocity field. The conditions required
to maintain a high correlation during the evolution are discussed. We have also seen that the 𝐸𝑏 decay mode is less sensitive to the value of θ than that of 𝐸𝑘. The relative contribution of 𝐸𝑘,𝐸𝑏, and the internal energy 𝐸𝑖 to the total energy 𝐸𝑡 is discussed in relation to the values of f, θ, and Re𝜎.
Related Papers
- Ladeinde, F. & Gaitonde, D.V. 2004. Magnetic Reynolds Number Effects on MHD Turbulence. Physics of Fluids Vol. 16 (6), pp. 1997-2021, https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1736674 (2004)
- Ladeinde, F. & Wu, J. 2002. Second Order Nonlinear Spatial Stability of Compressible Mixing Layers. Physics of Fluids, Vol. 14 (9), pp. 2968-2986, https://doi10.1063/1.1492284 (2001)
- Cai, X., O'Brien, E. E. & Ladeinde, F. 1998. Advection of Mass Fraction in Forced, Homogeneous, Compressible Turbulence. Physics of Fluids, Vol. 10 (9), pp. 2249-2259, https://doi.org/10.1063/1.869746, (1998)
- Ladeinde, F. Liu, W., & O'Brien, E. E., “Turbulence in Compressible Mixing Layers. ASME Journal of Fluids Engineering,” Vol. 120, No. 1, 1998, pp. 48-53 https://doi:10.1115/1.2819659 (1998)
- Cai, X., O'Brien, E. E. & Ladeinde, F. 1997. Thermodynamic Behavior in Decaying, Compressible Turbulence with Initially Dominant Temperature Fluctuations. Physics of Fluids, Vol. 9 (6), pp. 1754, https://doi10.1063/1.869292 (1997)
- Ladeinde, F., O'Brien, E. E. & Cai 1996. An Efficient Parallelized ENO Procedure for Direct Numerical Simulation of Turbulence. The Journal of Scientific Computing, Vol. 38 (11), pp. 215-242, https://doi10.1007/bf02088815 (1996)
- Cai, X., O'Brien, E. E. & Ladeinde, F. 1996. Uniform Mean Scalar Gradient in Grid Turbulence: Asymptotic Probability Distribution of a Passive Scalar, Physics of Fluids, Vol. 8 (9), pp.2555-2558, https://doi10.1063/1.869038 (1996)
- Ladeinde, F., “Supersonic Flux-Split Procedure for Second Moments of Turbulence,” AIAA Journal, Vol. 33, No. 7, pp. 1185-1195. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.12544. (1995)
- Ladeinde, F., O'Brien, E. E., Cai, X., & Liu, W. 1995. Advection by Polytropic Compressible Turbulence. Physics of Fluids, Vol. 48 (11), pp. 2848-2857, https://doi.org/10.1063/1.868661 (1995)